

 Knowledge Base +
Knowledge Base +  2023.12.08
2023.12.08Let's start with the fundamentals before delving into Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a details. An Ethernet cable is a network cable frequently used to connect devices like computers, routers, network switches, and gaming consoles to LANs and the Internet. These cables transmit data through electrical signals, providing a stable and speedy connection.
Ethernet cables consist of four twisted copper pairs enclosed in a protective outer sheath. The twisted pairs help reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference, ensuring a stable connection. They are available in various lengths and colors, making them versatile for different networking needs.
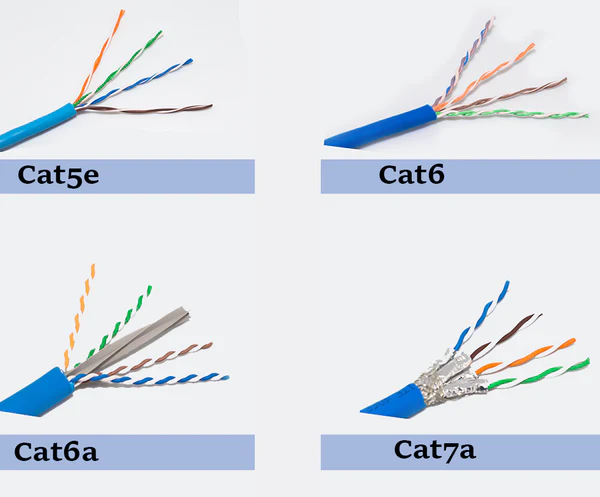
Cat5e, or Category 5e, is popular for many home and office setups. It's known for its affordability and decent performance. Cat5e cables can support data speeds of up to 1,000 Mbps (or 1 Gbps) and are suitable for most everyday internet tasks like web browsing, streaming, and online gaming. However, they may struggle with heavy data loads, making them less ideal for professional applications.
Cat6, or Category 6, Ethernet cables are an upgrade from Cat5e. These cables offer improved performance compared to Cat5e, with the ability to support higher data speeds. Cat6 cables can support data speeds of up to 10,000 Mbps (or 10 Gbps), making them a great choice for home and professional use. Cat6 Ethernet cables achieve this by utilizing stricter specifications and better insulation, reducing the risk of crosstalk and interference. If you need high-speed data transfer, such as 4K video streaming or large file transfers, Cat6 is an excellent option.
Cat6a, or Category 6a, Ethernet cables has twice the bandwidth capacity as Cat 6. They are designed to support data speeds of up to 10,000 Mbps (10 Gbps) like Cat6 cables but over longer distances compared to Cat6 cables. Cat6a cables improved shielding against crosstalk and interference, which makes them more resistant to electromagnetic interference, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments.
| Category | Number of pairs | Speed | Bandwidth Frequency | Distance | Cable type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cat5e | 4 pairs | 1000Mbps | 100MHz | 100m | UTP |
Cat6 | 4 pairs | 10Gbps | 250MHz | 55m | UTP/STP |
Cat6a | 4 pairs | 10Gbps | 500Mhz | 100m | STP |
Cat7 cable supports 10Gbps, but has been tested to transmit up to 50Gbps at 50 meters and 100Gbps at 15 meters. This cable has a standard frequency of 600MHz. Cat7 cable is stiff compared to previous generations due to the extensive shielding to reduce attenuation. Cat7 also requires special connectors.
Connecting an Ethernet cable is a straightforward process. Simply plug one end of the cable into your device (e.g., computer or router) and the other end into a compatible port on your network switch.
Ethernet cables transmit data between devices, allowing them to communicate and share information over a network. They are the backbone of wired internet connections.
Ethernet cable lengths can vary, but the maximum recommended length for reliable performance is 100 meters (approximately 328 feet). Beyond this length, signal quality may degrade.
The best Ethernet cable for you depends on your specific requirements. Cat6 and Cat6a are excellent choices for most users, offering a balance of performance and affordability.
Yes, Ethernet cables are highly recommended for gaming. They provide a stable and low-latency connection, which is crucial for online gaming.
Subscribe to the newsletter
for all the latest updates.
2-5# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Road, Shiyan Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen. China
