

 Knowledge Base +
Knowledge Base +  2023.12.01
2023.12.01QSFP28 (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable 28) DD (Double Density) are both types of transceiver modules used in high-speed data communication, particularly in networking and data center environments. The main difference between the two lies in their form factor and the number of electrical lanes they support.
QSFP28 is a small form-factor transceiver module that supports four lanes of high-speed data transmission, typically used for 100Gbps Ethernet and InfiniBand applications. It is widely used in networking equipment, such as switches and routers.
DD, on the other hand, stands for Double Density and refers to a newer form factor that supports eight electrical lanes for higher speed and greater bandwidth. DD transceivers are designed for use in high-speed interconnects, such as 400Gbps Ethernet and InfiniBand applications.
In summary, the main difference between QSFP28 and DD lies in their form factor and the number of electrical lanes they support, with DD offering higher speed and bandwidth capabilities compared to QSFP28.
Form factor & connectors
The term "form factor" refers to the standardized size and shape (or footprint ) of the optic, but other design features also help create each standard's definition. While there are many different transceiver form factors to consider, a few standards are more universal than the others.
Which you need is primarily determined by what form factors are compatible in the switch or router the optic is to be plugged in to, so it is always good to check what your system accepts.

AddOn's SFP-10G-SR-S-AO Cisco Compatible 1G SFP+ 40km LC Transceiver
Without the right form factor for your network environment, the optic may not fit into your switch or router at all. If it does connect, it may have impaired performance.
Can I use 100G QSFP28 port based with 40G QSFP+ transceiver?
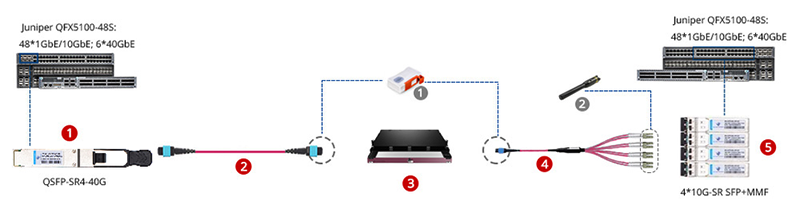
Most Switches, Network Packet Broker (NPB), and other Network Element allow the use of 40G QSFP+ optics within QSFP28 slot to support 10G using fanout/Breakout cable or 40G Multimode straight conectivity using MTP to MTP fiber cable.
SFP vs SFP+ vs XFP vs QSFP+ vs CFP vs QSFP28 Differences
Through the above definitions of each type of fiber optic transceiver module, you may have a further understanding of them. Now, we are comparing these transeiver one by one.
SFP vs SFP+ (SFP+ vs SFP): Simple to understand, SFP+ is an updated vision
of SFP. SFP usually support 1.25Gbit/s to 4.25 Gbit/s while SFP+ supports data
rates up to 10 Gbit/s. When it comes to SFP vs SFP+, they have the same size and
appearance, but in a different standard which SFP is based on IEEE802.3 and
SFF-8472.
SFP+ vs XFP (XFP vs SFP+): In comparison to earlier XFP modules, SFP+ modules leave more circuitry to be implemented on the host board instead of inside the module. The size of SFP+ is smaller than XFP, thus it moves some functions to motherboard, including signal modulation function, MAC, CDR and EDC. XFP is based on the standard of XFP MSA while SFP+ is compliance with the protocol of IEEE 802.3ae, SFF-8431, SFF-8432.
SFP+ vs QSFP+: QSFP+ has four-channel SFP+ interfaces which can transfer rates up to 40Gbps. And of course, they have different standards.
CFP vs QSFP+: QSFP+ (Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable Plus) modules offer customers a wide variety of high-density 40 Gigabit Ethernet. The CFP is a hot-pluggable transceiver module form factor that supports a wide range of 40Gb/s and 100Gb/s applications such as 40G and 100G Ethernet.
Related
Does QSFP28 support 40G
What are the different types of 40G QSFP
Are QSFP and QSFP28 compatible
Subscribe to the newsletter
for all the latest updates.
2-5# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Road, Shiyan Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen. China
