

 Knowledge Base +
Knowledge Base +  2023.12.08
2023.12.08Fiber optics offers faster speeds than Ethernet cable because it utilizes light signals to transmit data, while Ethernet cable uses electrical signals. Light travels much faster than electricity, allowing fiber optics to transmit data at higher speeds. Additionally, fiber optics can handle higher bandwidths and have lower latency compared to Ethernet, making them more efficient for transmitting data quickly.
1, the transmission loss of optical fiber is low, the transmission loss of cable is high.
2, fiber optic transmission bit rate is much lower than the bandwidth of the optical signal (signal amplitude down to the highest frequency before the available is called the bandwidth), the bit rate transmitted in the cable has been close to the bandwidth of the electrical signal, the electrical signal frequency, if you then improve, will lead to a further increase in loss, resulting in a decline in transmission distance.
3, the rate of optical signals lies in the optical module of the laser switching frequency and the processing rate of the digital circuit, the rate of cable transmission signal limit lies in the cable signal bandwidth.
Because of the above points, the rate of cable transmission is slower than optical fiber.
Fiber-optic communication requires optical fiber and optical modules, cable communication requires cable and physical layer chip, the cost of these two systems have their own optimal rate range and optimal distance range, in the low-speed (10 megabytes to 1G) short distance when the cable system cost is low, in the high-speed (1G to 400G) long-distance when the cost of fiber-optic system is low, but for the high-speed short-distance and low-speed long-distance, the cost of these two systems are not necessarily higher or lower, and need to be calculated specifically.
The power of optical signals in fiber optics attenuates by 6dB (3.98 times) for 10km; the power of voltage signals attenuates by 31.1dB (1,288 times) for a 100m CAT6A (for 10G Copper Ethernet) cable at the 250MHz frequency point.
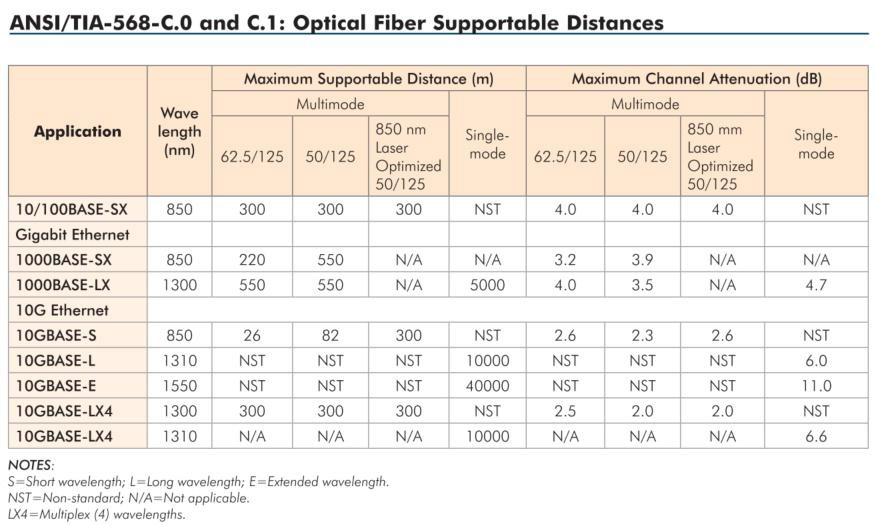
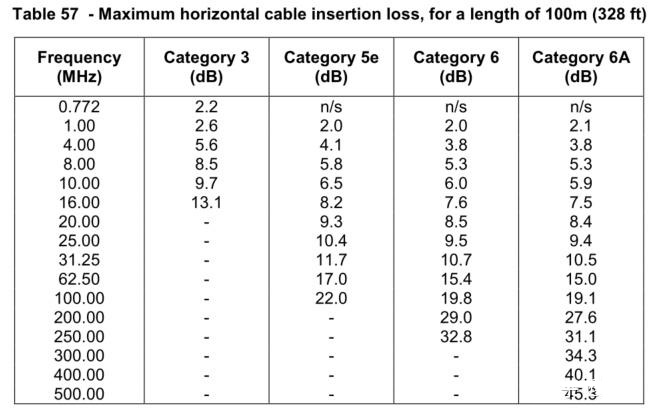
Performance is that optical fiber can easily do 10 kilometers, 40 kilometers of transmission distance, while the transmission speed can do 10G, 25G, 56G, now there are 100G optical modules; but the network cable transmission, 10G cable transmission limit can only do 100 meters, 5G cable transmission limit can only do 150 meters.
Fiber optic internal transmission of optical signals, optical fiber is only a transmission medium, the internal optical signals need to be sent and received by the optical module. Limitations on the optical fiber transmission rate is the optical module of the laser switching rate and processing chip processing rate.
At present, most of the optical modules are digital modulation, sending a specific wavelength of the light wave of the digital signal, that is, there is light intensity that is 1, no light intensity that is 0, the wavelength is generally 1310nm (corresponding to the frequency of 2300kG) or several other specific values. This determines that the frequency of the optical signal itself is not particularly critical, and will not be due to the limitations of Shannon's theorem leads to the wavelength and frequency of the optical signal will affect the actual transmission of the digital signal rate. The key to the fiber optic transmission rate is actually the switching frequency limit of the laser of the optical module and the rate limit of the corresponding digital processing chip.
Of course, there are also analog modulation or multiple wavelengths of simultaneous transmission of optical fiber and optical modules, but the cost of such systems is much higher, and is not the mainstream of long-distance transmission.
As for cables, that is, for network cables, the limit of their transmission rate is really limited by the cable as a transmission medium.
10G Ethernet, that is, 10GbE, the corresponding standard name is 10GBase-T, its transmission medium is CAT6A or CAT7 standard network cable, the transmission bandwidth of this cable is 500M, and can not directly transmit 10G digital signals, in order to allow the CAT6A cable to transmit the 10G ratio special, the cable uses 4 pairs of differential wires, and 10GbE's physical layer chip The physical layer chip of 10GbE sends not the digital signals of 0 and 1, but the analog signal of PAM16. By using 4 pairs of differential wires and the modulation signal of PAM16, the 500M bandwidth cable achieves the transmission rate of 10G.
10G Ethernet uses multiple pairs of differential lines with complex coding because it is too difficult and costly to directly increase the transmission bandwidth of the cable, so it has chosen to increase the complexity of the coding to achieve a higher data rate transmission on a lower bandwidth transmission medium.
Currently there are also 25G cable Ethernet, which requires a higher transmission bandwidth of the network cable, the need for thicker cores, denser twisted-pair spacing, better shielding, compared to 10G and greatly enhance the cost of the network cable.
Fiber-optic communication and network cable communication, both in the IEEE 802.3 standard has a detailed description of the optical fiber, cable, physical layer, data link layer, MAC layer have made a detailed definition.
The standard is not developed out of thin air, but the standards organization is constantly upgrading the rate target, cost target, each manufacturer to come up with their own optimal program for selection, and ultimately voted on the optimal program fixed as a standard.
Each manufacturer can be unified program, must be materials, technology, engineering, business after a variety of compromises to reach.
Specifically to the fiber and cable, that is, those mentioned above.
Subscribe to the newsletter
for all the latest updates.
2-5# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Road, Shiyan Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen. China
